 Is there DNA in urine? - Quora
Is there DNA in urine? - QuoraWarning: The NCBI website requires JavaScript to operate. Long-term Storm DNA extractionMarc Hilhorst1Clinical & Experimental Immunology, University of Maastricht, P.O. Box 5800, 6202 AZ Maastricht, Netherlands Ruud Theunissen1Clinical " Experimental Immunology, University of Maastricht, P.O. Box 5800, 6202 AZ Maastricht, NetherlandsHenk van Rie1Clinical " Experimental Immunology, University of Maastricht, P.O. Box 5800, 62munal Since DNA in the urine has been reported to deteriorate rapidly, this option is often not considered. To complete our DNA database in patients with vasculitis associated with ANCA, we try to extract DNA from the stored urine. MethodsThe urine was stored at the time of the renal biopsy of patients included in our regional renal biopsy database, who had given informed consent to a later study. Then they filtered, dialysis, concentrated and froze the dry, and finally settled and centrifuged. The DNA was extracted using the pure PCR template preparation kit (Roche Diagnostics). Then concentration and purity were determined by Nanodrop analysis and Quant-iT analysis. ResultsOne hundred and eighty-one patients were included with vasculitis associated with ANN. Of 114 patients (63%), DNA was available. Of 53 of the 67 remaining patients, there were stored urine. Of the 53 samples processed, 46 (86.8%) presented DNA with an average concentration of 258,7 ng/μL (range 33,2-529) with an average purity ratio of 1.81 (λ 260/280). ConclusionThe extraction of fresh urine DNA has been described earlier, producing DNA usable for PCR analysis in healthy subjects. Fresh urine storage at 4°C or lower temperatures results in significant DNA degradation, making DNA recovery more difficult with longer storage periods. In the current study, we showed that DNA could recover from the filtered, seasoned, concentrated and frozen dry urine that was then stored at room temperature. In addition, we demonstrate that this DNA could be used for PCR analysis. This method is useful when there is no other material of these patients. Background genetic factors have been studied by DNA analysis in many different diseases. In vasculitis associated with anti-neutrophilic cytoplasmic antibody (ANCA), the relevance of this analysis was shown in a study of genomedic association []. Traditionally, for these analyses, DNA recovers from soft layers. As reported to have the DNA in the urine deteriorated rapidly [], urine is usually not used for DNA analysis. We claim that it is possible to extract DNA from the urine properly stored from patients with glomerulonephritis associated with ANCA. MethodsThe Renal Registry of Limburg [] was sought to identify all the positive patients ANCA with glomerulonephritis glomerulonephritis puluciimmune to perform DNA analysis. The present study included patients from those who had no coats and/or soft tissues, but who had given their consent to further study. The Medical Research Ethics Committee of the Medical Center of the University of Maastricht approved the study. Exclusion criteria were concomitating kidney diseases such as diabetic nephropathy, thin GBM glomerulopathy or anti-GBM glomerulonephritis. At the time of kidney disease, the urine of patients was filtered through a paper filter. The urine was then dilated and concentrated in a Proflux M12® (Millipore, Billerica, MA, USA). The concentrated and diluted urine was subsequently frozen in a liquid nitrogen bath and dried in a Beta 1-8 LD® freezer (Christ, Osterode, Germany). Samples were subsequently stored at room temperature until use. To do this, the dry urine of 0.2 grams of frost was resolved in 20 ml of MilliQ and left it stirring during the night to 4°C. The next centrifuge the urine samples for 10 minutes to 10000 g. We extracted DNA using the pure PCR template preparation kit (Roche Molecular Diagnostics, Mannheim, Germany). Briefly, the supernatant was decanted and the sediment dissolved in protein K of 50 μL in 1 mL of binding damper (6 M guaninidine-HCl, 10 mM urea, 10 mM Tris-HCl, 20% Triton X-100, pH 4.4). After an incubation of ten minutes to 56°C, 100 μL of iso-propanol was added and the solution was centrifuged through a filter containing fiberglass for 1 minute to 8000 g. The filter was then centrifuged with 500 μL of inhibitor removal damping (5 M guaninidine-HCl, 20 mM Tris-HCl, 45% ethanol, pH 6.6) for 1 minute to 8000 g and washed three times with a wash damper (20 mM NaCl, 2 mM Tris-HCl, 80% ethanol, pH In addition, DNA was measured using Quant-iTTM Picogreen® dsDNA test. This is an ultrasensible fluorescent nucleic acid stain to quantify small amounts of double stranded DNA []. Results In the current study, 181 consecutive patients with glomerulonephritis associated with ANCA were included. Of 114 patients (63%) DNA was available. Of the remaining 67 patients, 24 hours of frozen dry urine were available. The freezing of the dry urine of these patients had been stored at room temperature for an average time of 16 years (between 6 and 28). Of the 53 samples processed, 46 (86.8%) presented DNA with an average concentration of 258,7 ng/μL (range 33,2-529) with an average purity ratio of 1.81 (λ 260/280) measured in a Nanodrop® 2100. Eleven samples were more diluted for picogrene analysis. These samples were found to contain DNA at an average concentration of 40 ng/μ L in the Nanodrop® 2100 and an average concentration of dsDNA of 23.35 ng/μL L for picogreen analysis. Polymorphisms in several genes (CTLA-4, PD1) could be determined in 38 (82.6%) of these samples [] (Figure) ). Linear regression showed that the amount of DNA extracted from the urine was not correlated with the amount of proteinuria at the time of urine storage (R2 = 0.02; p = 0.34) or the length of time the urine was stored (R2 = 0.08; p = 0.55). In addition, Chi-square's analysis showed that gender is not important (p = 0.8) by signaling 87.5 per cent of men and 54.5 per cent of women. Finally, the gel electrophoresis with urine DNA PCR and three-patient soft layer products showed similar bands in varying magnitude (Figure) ). CTLA-4 +49 polymorphism analysis of 5 patients in DNA recovered from urine. Patient 1 had AG genotype, patient 2 AA, patient 3 not detectable, patient 4 GG and patient 5 AA. DNA from the urine and DNA from the fat of three patients. The agarose gel shows signs of CTLA-4 +49 polymorphism from these three patients. Patient 1 with fat DNA in 1 and urine DNA in 2 (GG); patient 2 with fat DNA in 3 and urine DNA in 4 (AA); patient 3 with fat DNA in 5 and urine DNA in 6 (AA). The DNA of the urine and the DNA of buffycoat produces similar signals in varying magnitude. DiscussionThe extraction of fresh urine DNA has been described earlier, giving the DNA used for PCR analysis in up to 35% of healthy men and up to 75% of healthy females [,]. Fresh urine storage at 4°C or lower temperatures results in significant human DNA degradation, resulting in low recovery rates during long-term storage [-]. When urine is stored at -20°C, about 75% of DNA degradations within 28 days [,], making it difficult to recover quantitatively after this period []. A temperature of -80°C improves recovery up to 28 days of storage, but increases storage costs [,]. It is important, however, that Fernandez-Soto et al. reported that it was not possible to recover DNA for PCR analysis of urine samples stored at -80° C after storage for 18 months up to 7 years []. Sodium azida addition or EDTA has been reported to improve DNA recovery [,,]. However, no study has reported data on the recovery of DNA from samples stored at -80°C with the addition of azida or EDTA. However, at all temperatures, the recovery of human DNA after longer periods of storage seems to be difficult. In the current study, we show that human DNA could recover from frozen dry urine that could be used for PCR analysis, after an average storage period of 16 years at room temperature. The analysis by eosin and hematoxylin (H patientE) showed damaged but intact cells with intact nuclei in the urinary sediment. Within these cells, the leukocytes were present that positively stained with anti-CD45 (no data were shown). The cells are grouped around debris in the sediment, suggesting that these debris may have protected the cells from degradation during all these years. Conclusion We conclude that in the case of deceased or lost patients to follow, DNA can recover from dry urine that has been stored for a period of up to 28 years. Abbreviations DNA: Deoxiribonucleic acid; ANCA: Anti-neutrophilic cytoplasmic antibodies; GBM: glomerular basal membrane; PCR: Polymerase chain reaction. Competing interests The authors declare that they have no competing interests. Contributions from the authors MH, RT and HvR carried out DNA extraction and critical revision of the manuscript. MH and JWCT contributed to the concept of study, data interpretation, draft of the manuscript and critical revision of the manuscript. PvP contributed to the concept of study, data interpretation and critical revision of the manuscript. All authors have given the final approval of the manuscript to be presented. Pre-publication history The pre-publication history of this document can be accessed here:Recognition We thank N. Bijnens and P. Heerings-Rewinkel (Laboratory of Clinical Immunology, Maastricht University Medical Center, Maastricht) for the assistance. This study was carried out for the Register of Renas de Limburg. ReferencesFormats: Share , 8600 Rockville Pike, Bethesda MD, 20894 USA
Accessibility links Search modes Search resultsCare data. What is Urine? How do you do Urine? Can anyone offer any advice or method to extract DNA... how can I isolate the DNA from the urine? ResearchGateHuman Urine Contains Small, 150 to 250 Nucleotide-Sized .. .

Is there DNA in urine? - Quora
Does Urine Have DNA and Can You Extract It from a Sample?
You season 2 spoilers: Will Joe be exposed by DNA evidence? | TV & Radio | Showbiz & TV | Express.co.uk
DNA Is In All of Your Cells Body Fluids and Tissues Blood Semen Saliva Perspiration Tissue Bones and Teeth Hair (if there is tissue on the root) Urine, - ppt download
Does Urine Have DNA and Can You Extract It from a Sample?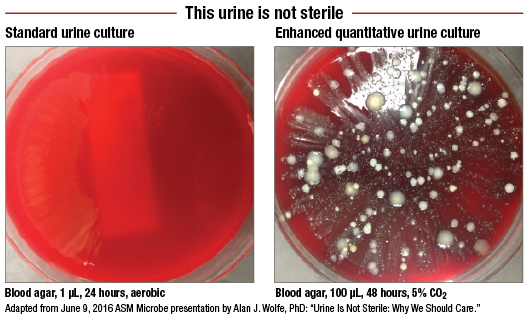
Missed UTIs? 'Enhanced cultures' suggest so | CAP TODAY![18 Questions I Have For]()
18 Questions I Have For "You" On Netflix
Does Urine Have DNA and Can You Extract It from a Sample?
Human Biology Tests Isolated Sperm Blood Urine Stool DNA Icon.. Royalty Free Cliparts, Vectors, And Stock Illustration. Image 96716334.
Is There DNA In Urine? - Forex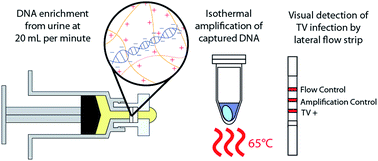
Rapid electrostatic DNA enrichment for sensitive detection of Trichomonas vaginalis in clinical urinary samples - Analytical Methods (RSC Publishing)
Pin on Science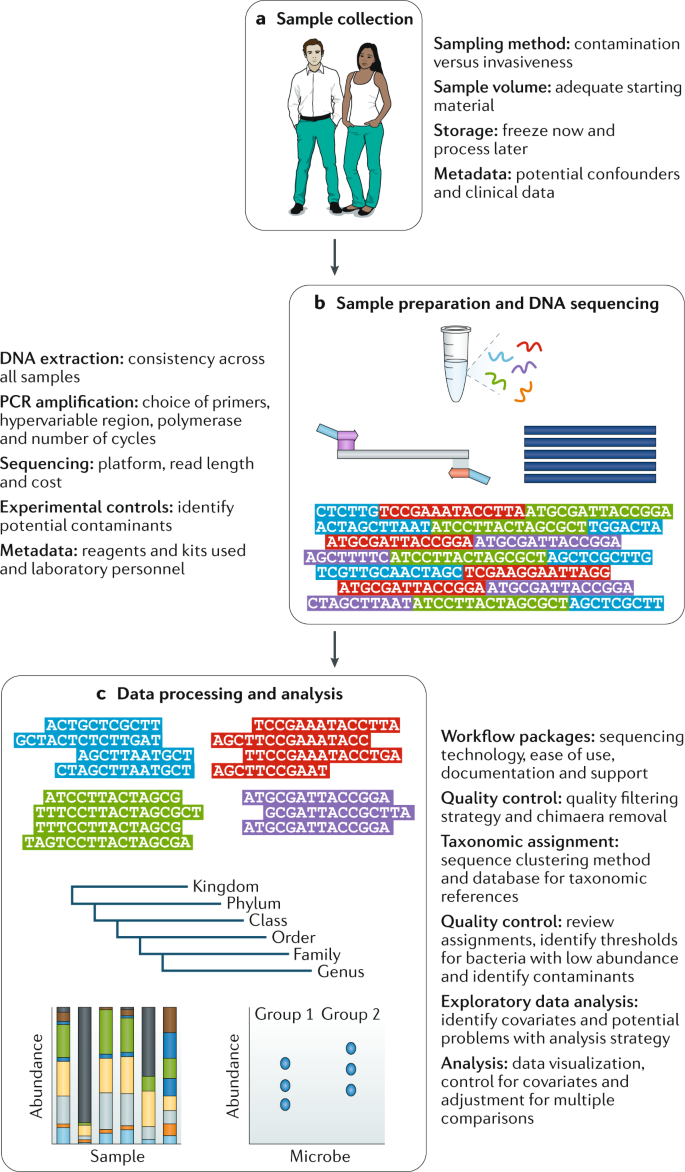
Community profiling of the urinary microbiota: considerations for low-biomass samples | Nature Reviews Urology
Interactions That Hold DNA Together
A protocol for urine collection and storage prior to DNA methylation analysis
PDF) DNA Hyper-methylation Profile of Multiple Genes involved in Bladder Cancer among Saudi Population
IJMS | Free Full-Text | ITIH5 and ECRG4 DNA Methylation Biomarker Test (EI-BLA) for Urine-Based Non-Invasive Detection of Bladder Cancer | HTML
Does Size Matter? Comparison of Extraction Yields for Different-Sized DNA Fragments by Seven Different Routine and Four New Circulating Cell-Free Extraction Methods | Journal of Clinical Microbiology
Does Urine Have DNA and Can You Extract It from a Sample?.jpg)
Urine culture - Lab Tests Online AU
Clinical significance of negative and equivocal urinary bladder cytology alone and in combination with DNA image analysis and cystoscopy - Katz - 1997 - Cancer Cytopathology - Wiley Online Library
Detection of Promoter DNA Methylation in Urine and Plasma Aids the Detection of Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer | Clinical Cancer Research
Genes and Chromosomes - Fundamentals - MSD Manual Consumer Version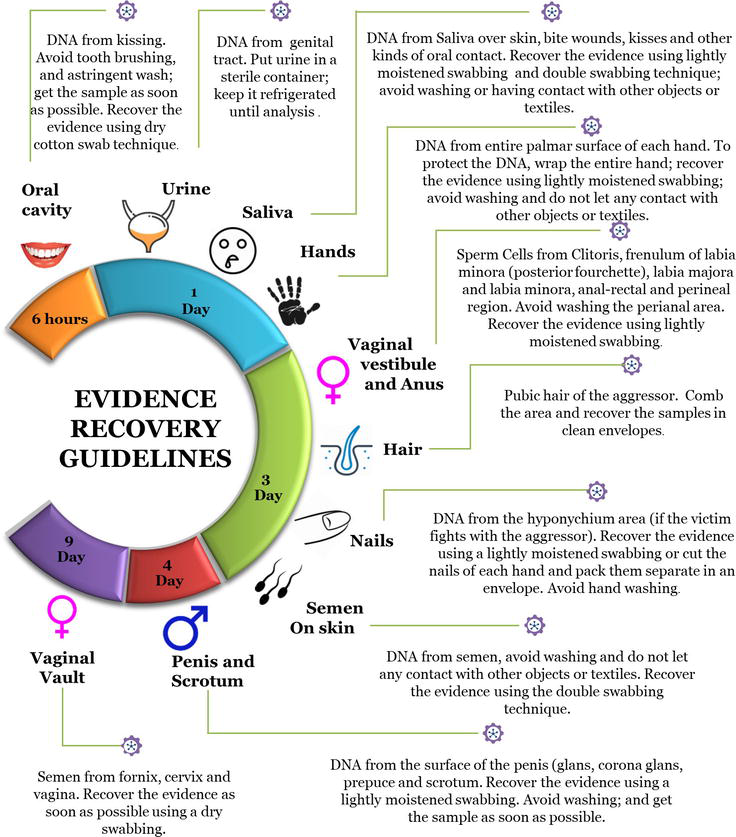
Biological Evidence Analysis in Cases of Sexual Assault | IntechOpen
Urine is not sterile, and neither is the rest of you | Science News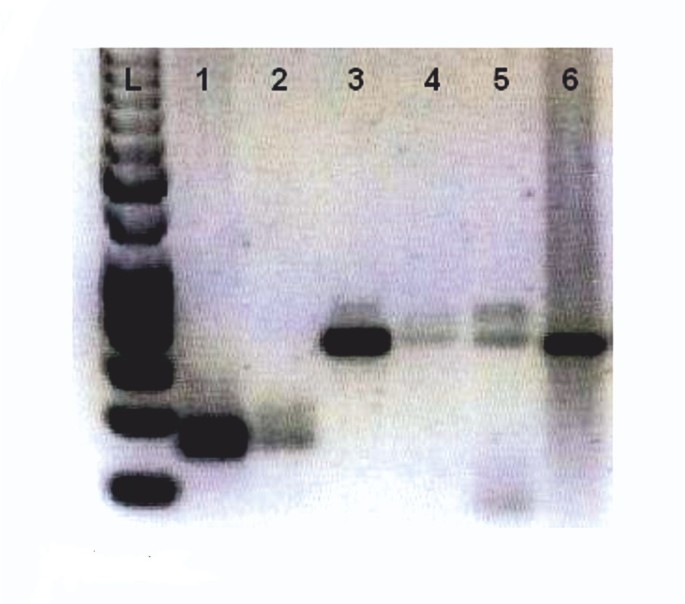
DNA extraction from long-term stored urine | BMC Nephrology | Full Text
Three Key Steps to Effective DNA Swab Collection at Crime Scenes
DNA in Urine Can Reveal Disease | Live Science
Detection of Promoter DNA Methylation in Urine and Plasma Aids the Detection of Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer | Clinical Cancer Research
How stress can change your DNA - Science in the News
Five ways mapping the human genome has changed cancer care | CTCA
One Company Makes Almost All the Home DNA Test Spit Tubes - Bloomberg
Female UTIs – Your Burning Questions Answered | Health Plus
Toward standards in clinical microbiome studies: comparison of three DNA extraction methods and two bioinformatic pipelines | bioRxiv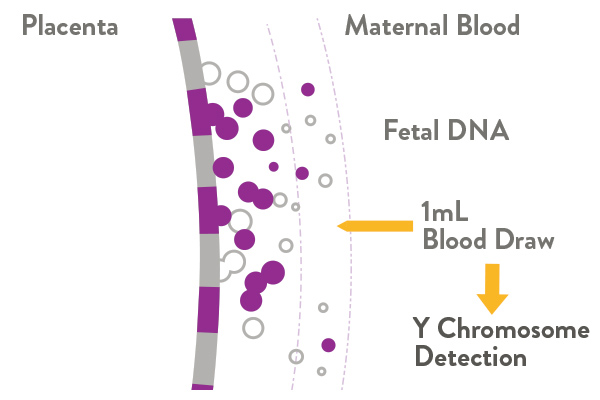
Are Pregnancy Urine Gender Tests Accurate? | SneakPeek®
Buccal Swab - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics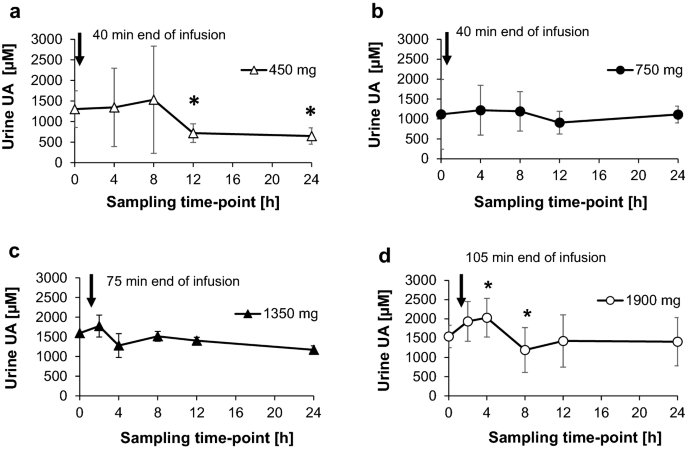
In-Vivo Degradation of DNA-Based Therapeutic BC 007 in Humans | SpringerLink
High Resolution Size Analysis of Fetal DNA in the Urine of Pregnant Women by Paired-End Massively Parallel Sequencing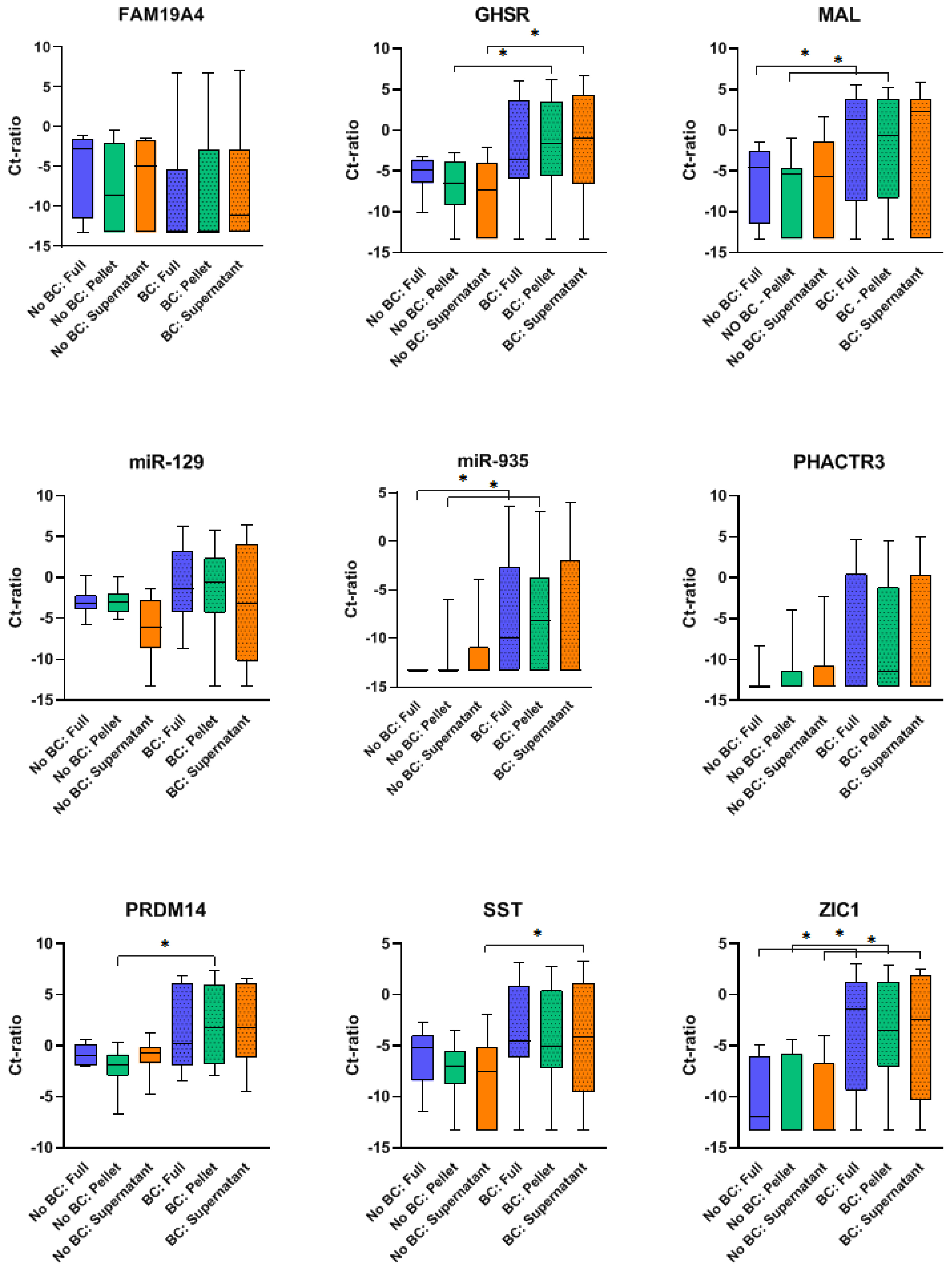
Cancers | Free Full-Text | Comparative Analysis of Urine Fractions for Optimal Bladder Cancer Detection Using DNA Methylation Markers














.jpg)


















Posting Komentar untuk "does urine hold dna"