Sickle Cell Disease In Africa
Sickle cell disease in africa. More than 10000 children with sickle cell disease die each year before they reach their fifth birthday in Tanzania East Africa. Sickle cell disease in Africa. However with increasing awareness of the condition and economic and epidemiologic transition increasing numbers are surviving.
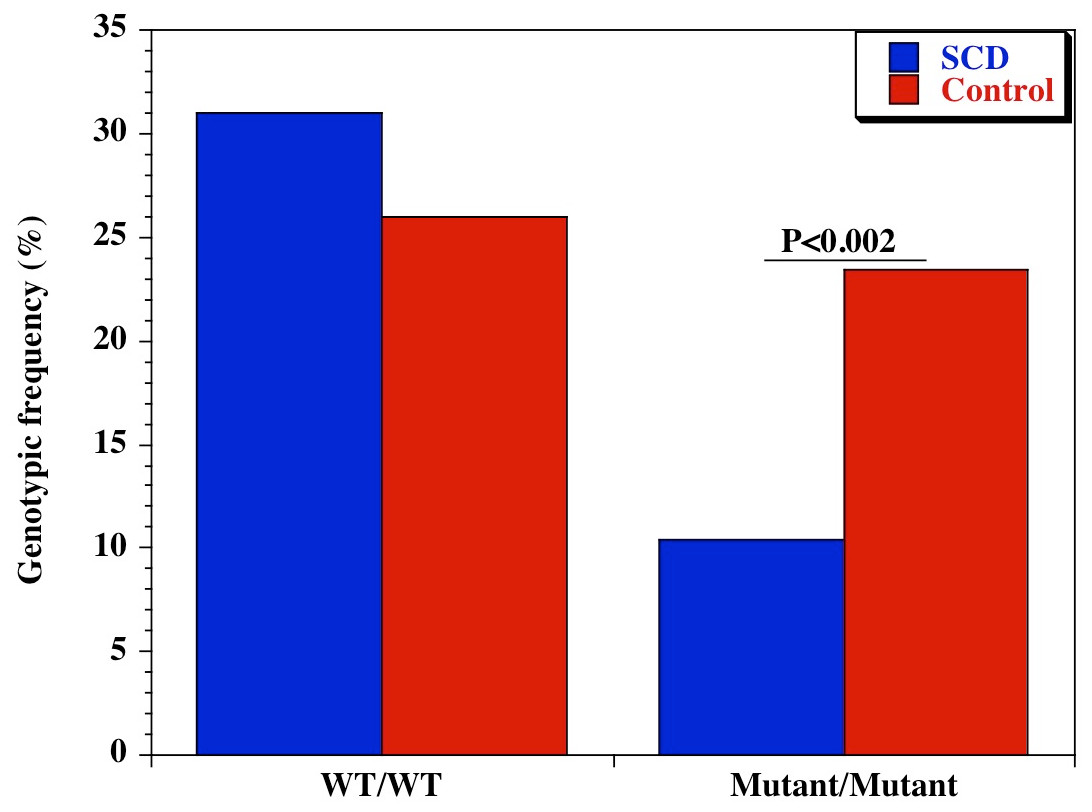
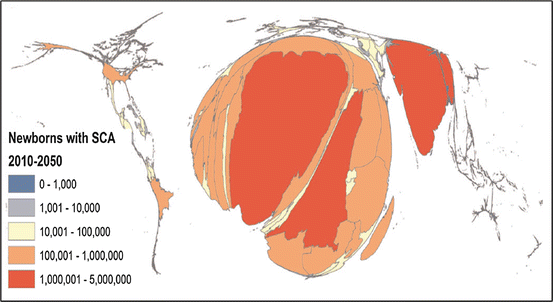
In the WHO African region an estimated 5 of deaths in children younger than 5 years result from sickle cell disease and up to 16 of deaths in some west African countries. Researchers are working to change that however with several studies. The worlds SCD population is concentrated in three countries.
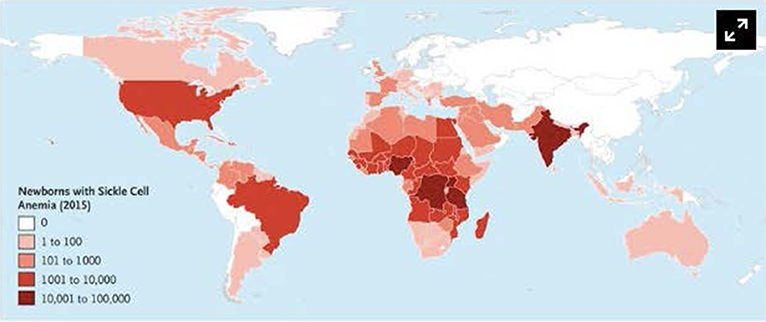
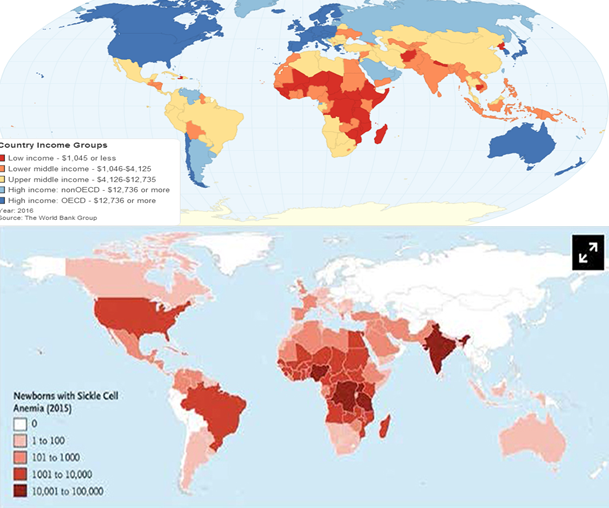
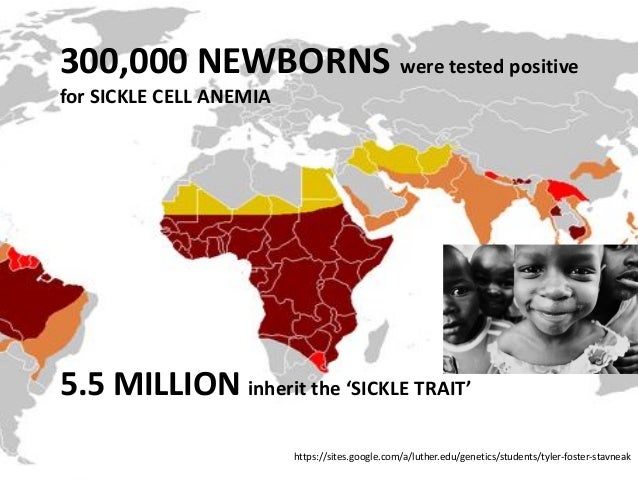
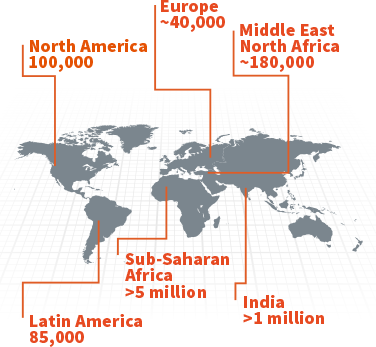
About 44 million people have sickle cell disease while an additional 43 million have sickle cell trait. Sickle cell disease is a major public health problem with over 200000 babies born per year with SCD in Africa. Sickle cell disease SCD is common throughout much of sub-Saharan Africa affecting up to 3 of births in some parts of the continent.
The World Health Organization has declared Sickle Cell Anemia SCA a public health priority. The most common form of SCD is caused by homozygosity for the β-globin S gene mutation SS disease. 80 percent of them die before their fifth birthday.
It is the most prevalentgenetic disease in the WHO African Region. 1 The UN recognised sickle cell disease as a public health priority in 2009. Research needed to inform policy decisions.
Sickle cell disease one of the worlds most common genetic disorders occurs when. Given the high burden of Sickle Cell Disease SCD in Africa the Sickle Pan-African Research Consortium SPARCO funded by the US National Institute of Health has over the last four years developed the infrastructure for future research in SCD and strengthened skills in health services. Approximately 80 of all children born with SCD are in sub-Saharan Africa.
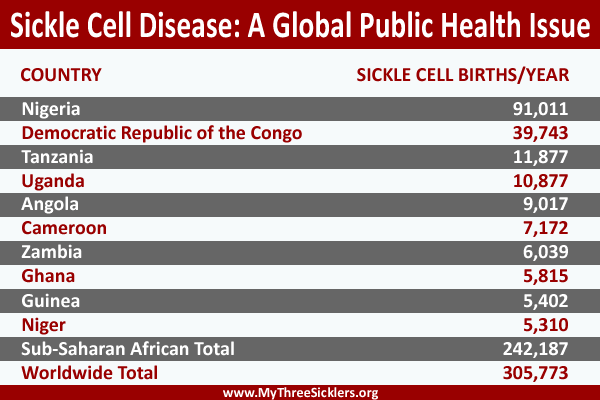
Sickle cell disease SCD has recently been recognised as a problem of major public-health significance by the World Health Organization. In Africa at least 240000 children are born each year with sickle cell disease.
It is the most prevalentgenetic disease in the WHO African Region.
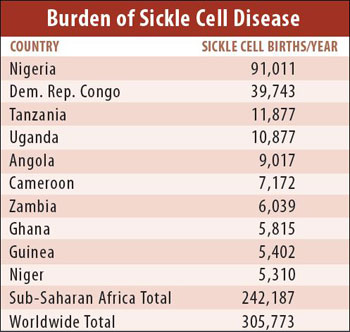
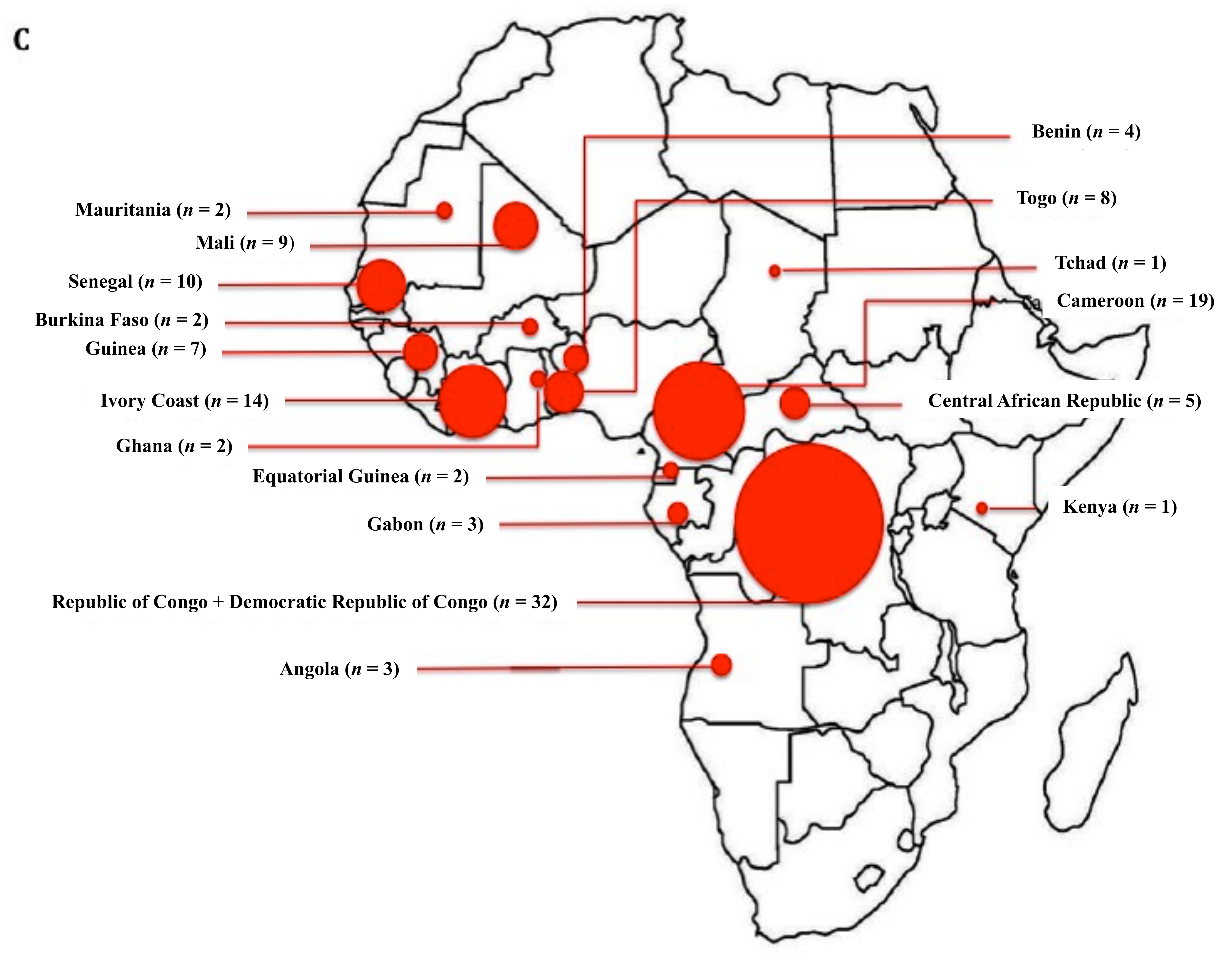
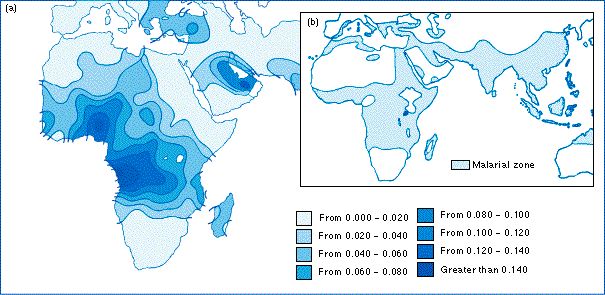
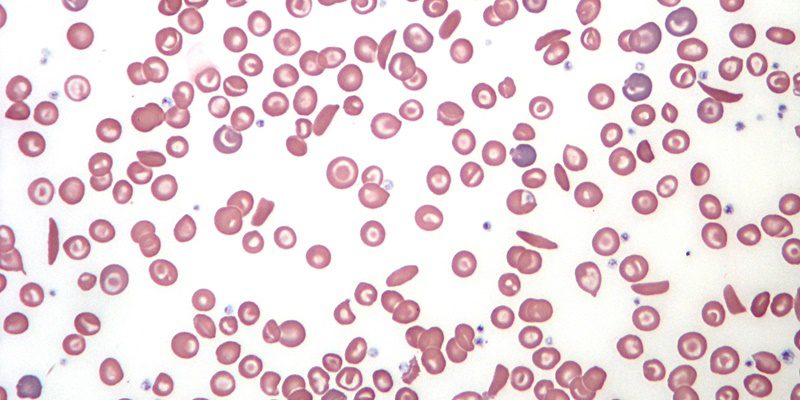
Nutritional perspectives on sickle cell disease in Africa. Inflammation haemolysis microvascular obstruction and organ damage characterise the clinical expression of the disease. Sickle-cell Disease SCD is an inherited disorder of haemoglobin. Nigeria India and the Democratic Republic of Congo figure 1 where the disease affects up to 2 percent of the population and the carrier prevalence rate sickle cell trait is as high as 10 to 30 percent. Sickle cell disease is a major public health problem with over 200000 babies born per year with SCD in Africa. However with increasing awareness of the condition and economic and epidemiologic transition increasing numbers are surviving. There are 300000 birthsyear over 75 in Africa with estimates suggesting that 6 million Africans will be living with SCA if average survival reaches half the African norm. More than 10000 children with sickle cell disease die each year before they reach their fifth birthday in Tanzania East Africa. 1 The UN recognised sickle cell disease as a public health priority in 2009.
About 80 of sickle cell disease cases are believed to occur in Sub-Saharan Africa. The worlds SCD population is concentrated in three countries. Sickle cell disease in Africa. About 80 of sickle cell disease cases are believed to occur in Sub-Saharan Africa. 1 The UN recognised sickle cell disease as a public health priority in 2009. This mutation arose 7300 years ago in a single child living in the Sahara region. Despite the fact that 70 of sufferers live in Africa expenditure on the related care and research in the continent is negligible and most advances in the understanding and management of this condition have been based on research conducted in the North.




























Posting Komentar untuk "Sickle Cell Disease In Africa"